Cybersecurity Key Business Ideology
Key Concepts:
Business Impact Analysis (BIA). BIA predicts the consequences of a disruption to your business function(s) and process, and then gathers information needed to develop recovery strategies. Potential loss scenarios should be identified during a Risk Assessment. Include not only policies but determinations of terms like MTD, RPO, and RTOs. MTD is basically how long can your business system be offline before the data is worthless. RTO is the amount of time it takes a business to recover the business systems(s). RPO defines how much data loss the business can withstand or, more simply, how often items are being backed up and or replicated in your database. A BIA gives you a prioritization of bringing your business systems back to life.
Confidentiality (C), Integrity (I), and Availability (A) or CIA. The (National Institute of Science and Technology (NIST) uses a CIA triad that represents the three pillars of information security: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability, as follows:

Figure 1 BUSINESS DATA
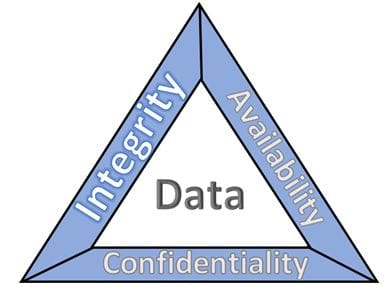
Confidentiality
Preserving authorized restrictions on business information access and disclosure, including means for protecting personal privacy and proprietary information for the business. In cybersecurity, confidentiality refers to the safeguarding of business data and information against unauthorized disclosure, access, or usage. It is one of the core principles of cybersecurity. Confidentiality is important to protect personal and proprietary business information from undesired entities. Cyber professionals depend on confidentiality to protect business data, networks, and computer systems from attack.
Integrity
Guarding against improper business data information modification or destruction and ensuring information non-repudiation and authenticity. Non-repudiation is a regulatory notion commonly used in cybersecurity and refers to the service that confirms the origin and integrity of data. It assures that no party can deny sending or receiving a communication using encryption and digital signatures. It cannot also contest the legitimacy of its digital signature on a document.
Availability
Ensuring timely and reliable business data access to and use of business data information. Availability in cybersecurity is the ability of authorized users to access and use business data and systems as intended. It is one of the three basic functions of security management that are present in all systems. Availability is important for maintaining the business operations and productivity of any business.
